In an earlier post I took a look at how to setup EVE-NG to get access to virtualized network devices and topologies. This post is going to take a look at how to setup GNS3 systems to allow access.
In the overall topology that is a "home" network sits a device that supports a routing protocol, usually either OSPF or BGP. What is known to work at an inexpensive price point is the Ubiquiti EdgeRouter X.
GNS3 Setup
This post is not a post on how to setup GNS3, it is meant to help you start to access devices. This tutorial is running a GNS3 VM on a remote host. Take a look at the GNS3 docs on how to install GNS3 specifically.
GNS3 Configuration
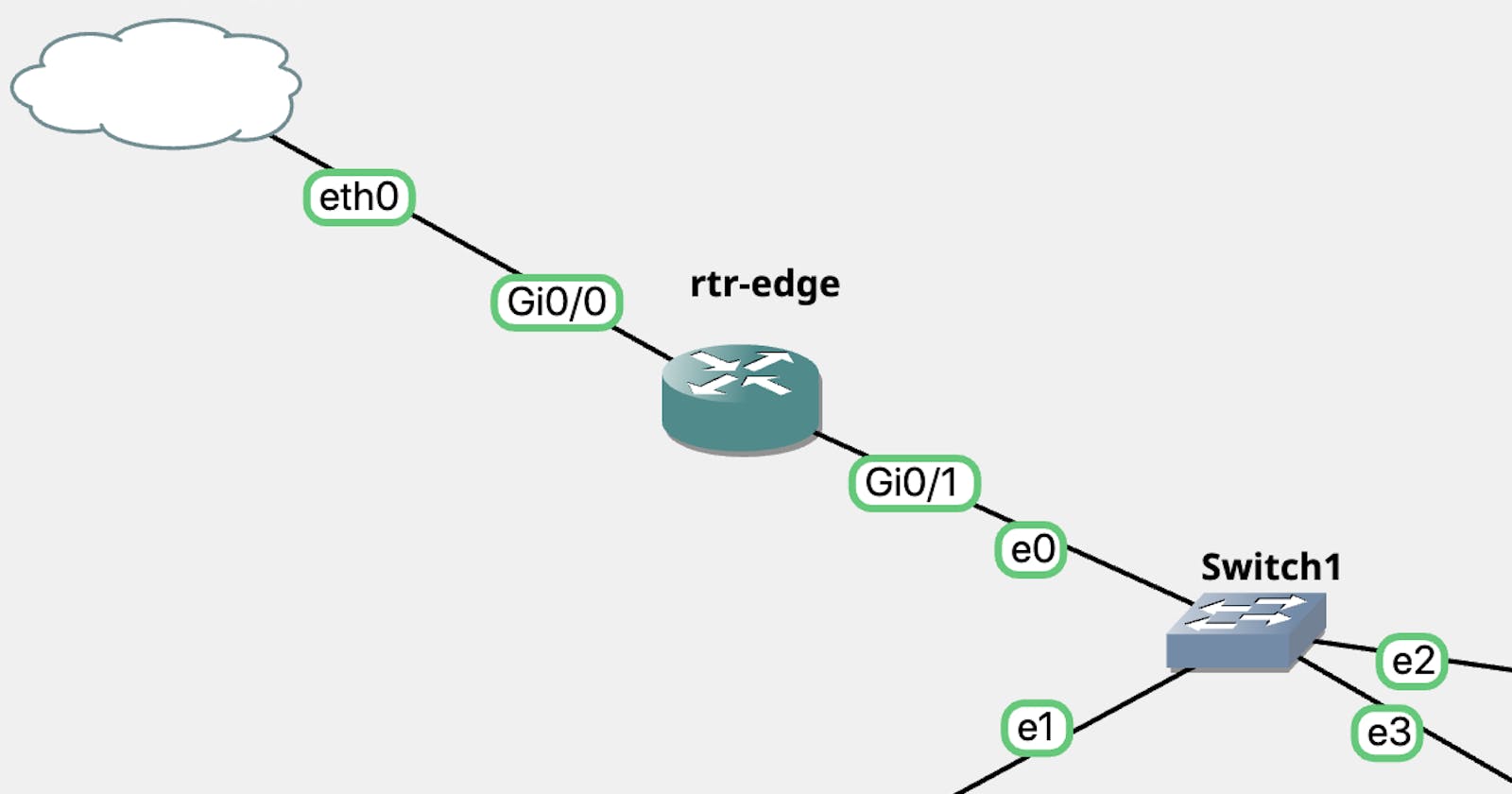
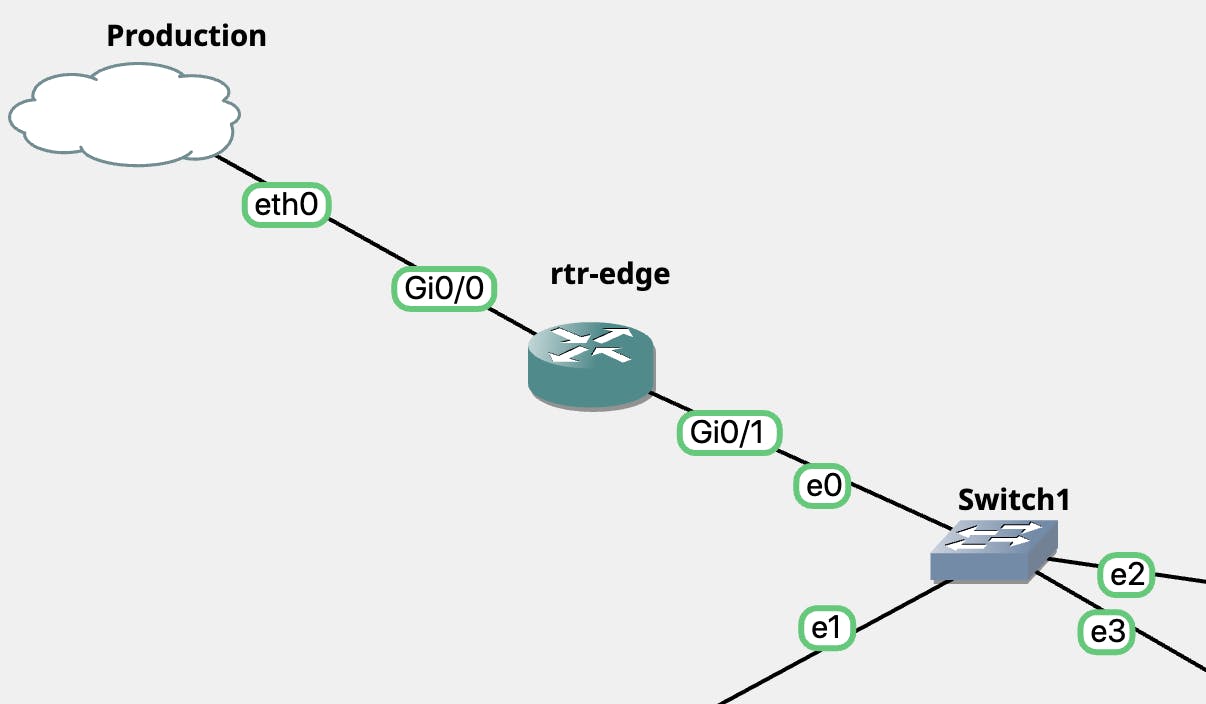
The topology item used to create the connection to the production network is the device type of Cloud. Add a cloud with the general connection and the device will have connectivity to your local network.
Next setup a router (in this instance using a Cisco vIOS image - licensed item). Connect that device to the cloud that was added to the topology. In this particular setup, DHCP is being used.
Router Configuration
rtr-edge#show run interface GigabitEthernet0/0
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 110 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
ip address dhcp
duplex auto
speed auto
media-type rj45
no cdp enable
end
With the device getting an address, the device also gets a floating default static route imported to match the DNS request:
rtr-edge#show ip route
Codes: L - local, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route, H - NHRP, l - LISP
a - application route
+ - replicated route, % - next hop override, p - overrides from PfR
Gateway of last resort is 192.0.2.1 to network 0.0.0.0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 [254/0] via 192.0.2.1
192.0.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
L 192.0.2.163/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
Verify that you have access to the Internet by using ICMP to test.
rtr-edge#ping 1.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 1.1.1.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 13/16/18 ms
Setup Automation
By using OSPF you are able to setup networks and advertise them back into your "production"/"home" network. With the network being advertised you can then setup your hosts with addressing that would have access from the network.
It is recommended that you test SSH/API connectivity into the GNS3 environment manually.
Summary
With the tools of GNS3, EVE-NG, Cisco CML, and VRNetLab you have significant choice in looking at tools that will help you to level up your skills in Network Automation.
Hope that this may help you out in some way!
Josh